Control Plane Architecture of Software Defined Coalitions
Military / Coalition Issue
Military missions require the use of infrastructure assets including communication links, computational servers, data storage, databases, sensors and other resources. Dynamicity and agility of military operations demand near real-time configuration, re-configuration and provisioning of these resources, while supporting efficient and robust sharing of assets across armed forces or coalition partners. State-of-the-art techniques cannot currently achieve this.
Core idea and Key Achievements
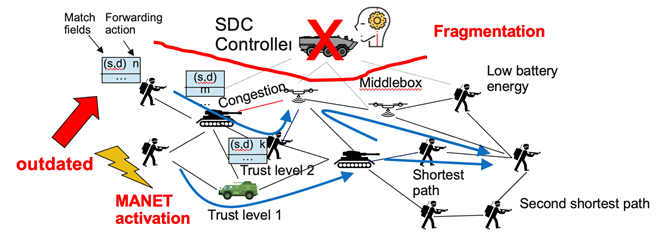
A new architecture called Software Defined Coalitions (SDC) has been developed, which extends the existing Software Defined Networking (SDN), to address the above issue. With SDC, the network control logic is implemented as software at the SDC controller which is programmable to enable rapid configuration for mission objectives. The controller maintains also a conceptually centralized view of the network status that can be valuable for many networking applications. However, due to high network dynamics the controller may be fragmented from the nodes it manages rendering impossible their reconfiguration. An approach that improves the robustness of SDC is therefore needed.
Key achievements include the development of:
- Hybrid SDC/MANET (mobile ad-hoc network) architectures where the SDC controller can interface and dynamically switch the control mode to a distributed MANET protocol (e.g., OLSR) to handle network fragmentation events.
- Distributed verification mechanisms for discovery of the controller by the mobile nodes and switching the control mode accordingly.
- Algebra to support continuous and frequent network configuration updates by the SDC controller
- Novel paradigm to enable inter coalition coordination through the SDC controllers
- Testbed experiments with real mobile devices showing the benefits of hybrid SDC/MANET for dynamic routing and failover
Implications for Defence
The hybrid SDC/MANET architecture and accompanying mechanisms will enable defence to realise the concept of SDC even in the most challenging ad hoc network environments, reap the benefits of centralized and programmable network control and deliver intelligent cloud-like services involving multiple coalition enclaves that were impossible to realize by relying only to traditional MANET protocols.
Readiness and Alternative Defence Uses
This work is technology readiness level (TRL) 2/3. Many of the SDC techniques have been prototyped in practical systems or environments, including the demo Hybrid SDN/MANET. Further work will enhance the readiness of the new techniques for practical defence systems.
Resources and References
Samples of related publications include:
- Poularakis, Konstantinos, et al. “Bringing SDN to the mobile edge.” 2017 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced & Trusted Computed, Scalable Computing & Communications, Cloud & Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation (SmartWorld/SCALCOM/UIC/ATC/CBDCom/IOP/SCI). IEEE, 2017.
- Poularakis, Konstantinos, Qiaofeng Qin, Erich M. Nahum, Miguel Rio, and Leandros Tassiulas. “Flexible SDN control in tactical ad hoc networks.” Ad Hoc Networks 85 (2019): 71-80.
- Poularakis, Konstantinos, Qiaofeng Qin, Kelvin M. Marcus, Kevin S. Chan, Kin K. Leung, and Leandros Tassiulas. “Hybrid SDN control in mobile ad hoc networks.” In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), pp. 110-114. IEEE, 2019.
- Gokarslan, Kerim, Geng Li, Patrick Baker, Franck Le, Sastry Kompella, Kelvin M. Marcus, Vinod K. Mishra, Jeremy Tucker, Y. Richard Yang, and Paul Yu. “A Highly Reliable and Programmable Software Defined Coalition (SDC) Architecture using Multiple Control Plane Composition with Distributed Verification.”
- Xiang, Qiao, Jingxuan Zhang, Kai Gao, Yeon-sup Lim, Franck Le, Geng Li, and Y. Richard Yang. “Toward optimal software-defined interdomain routing.” In IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 1529-1538. IEEE, 2020.
- Li, Geng, Y. Richard Yang, Franck Le, Yeon-sup Lim, and Junqi Wang. “Update algebra: Toward continuous, non-blocking composition of network updates in sdn.” In IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 1081-1089. IEEE, 2019.
Organisations
Yale University, IBM US, UCL, Imperial College, ARL, Dstl