Framework for Modeling the Effect of Emotion on Uncritical Reasoning
Military / Coalition Issue
Understanding group mutability in the behavior of external groups, and how the spread of rumours or memes, together with the effect of interventions by coalition forces may affect the behavior in terms of dispiriting hostile groups and encouraging friendly groups.
Core idea and key achievements
Computational framework that holds a cognitive model of an individual operating within a group context, inspired by theories from social science. Individuals relate to in-groups and out-groups and have beliefs that are associated with emotions. Cognitive Appraisal Theory is used to evaluate incoming memes “pronounced” by external speakers on individual self-esteem taking account of their group relationships as indicated by social identity theory, and leading to an emotion in the individual. Appraisal is followed by a process of coping that seeks to handle the effects by either performing problem-focused (critical) or emotion-focused (uncritical) thinking, according to the current emotional state of the individual.
Scenario-based demonstration where populations of individuals move in a geographical space and interact with each other, seeking to spreading rumours or memes. Two methods for visualizing the results of the simulation: a geographic diagram of the movement of individuals with their affiliations and emotional levels; and a time series graph of key model variables, such as the reach of memes, average emotional levels, and membership of different groups.
Implications for Defence
Demonstrate mutable group behavior, and identify opportunities for monitoring and intervention.
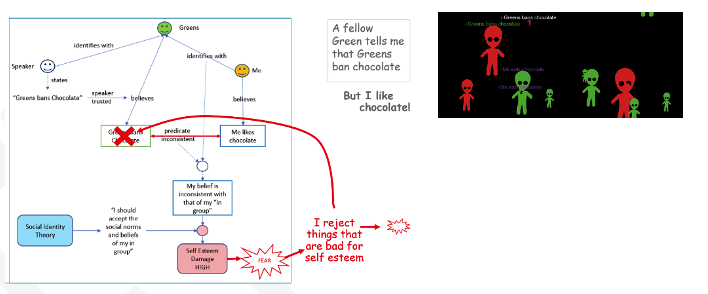
Social Identity Theory: I wish to follow the group norm. I like chocolate, but I am told that my group “Greens” is banning chocolate, which is inconsistent with my personal belief. This affects my self-esteem negatively and leads to fear. Uncritical thinking: I cope with the self-esteem damage by rejecting the statement that my group, “Greens ban chocolate.” The self-esteem damage and fear are diminished. However, my knowledge state is Inconsistent, since a trusted source is indicated something that I rejected. Critical thinking: I remove the premise (that I identify with the Greens) or (that the speaker is trusted) so that my belief is no longer inconsistent, and hence remove the self-esteem damage and fear.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
TRL 3. Computational framework and model with base functionality. Cognitive model runs within the Soar Cognitive Architecture as a set of reasoning processes and rules that handle beliefs and emotion. Simulation tool, Repast Simphony runs multi-agent simulations based on the integration of multiple instances of the cognitive agents.
Resources and references
- Mott, David, Troy D. Kelley, Cheryl Giammanco, Soheil Eshghi, and Yunfeng Zhang. “A Framework for Modelling the Effect of Emotion on Uncritical Reasoning ”, 2017 ICCRTS-KSCO.
- Mott, David, Troy D. Kelley, Cheryl Giammanco, Soheil Eshghi, and Yunfeng Zhang. “Demonstrating a Framework for Modelling the Effect of Emotion on Uncritical Reasoning” 2017 ICCRTS-KSCO.
Organisations
IBM UK, ARL DEVCOM, Yale University, IBM US