Predicting Spread of Negative Attitudes and Behaviors in Social Networks
Military / Coalition Issue
Understanding user behavior on a social network is a challenging problem. It is important to understand how this behavior changes in terms of the influencer, the influenced, and the temporal dimension.
Core idea and key achievements
This work uses utterance of curse words as a proxy for user behaviour. Utterance of curse words typically exhibit both temporal and spatial clusters, i.e., the propensity of a node in a social network uttering a curse work is highly dependent on the node’s neighbour uttering curse words in the recent past. This work introduces a new modelling technique, based on Graph LSTMs (Long Short-term Memory), that improves predictability of who and when will utter curse words next. Evaluations on the Twitter dataset show that considering network effects improves prediction performance by over 30%, in comparison with traditional statistical models such as the Hawkes Point Process.
Unlike prior efforts, this new model fundamentally captures the behavior both along the graph and the time dimension. Core to the construct is the graph convolution operator that convolves a signal (number of curse word utterances per unit time) over a neighborhood in a graph. Combined with a LSTM layer the model captures how the signal spreads over time on the graph structure. In addition, the new model supports what-if analysis in the form of predicting how changes to the graph structure or how initial point of infusion (who uttered the curse word first) can influence its overall spread on the social network.
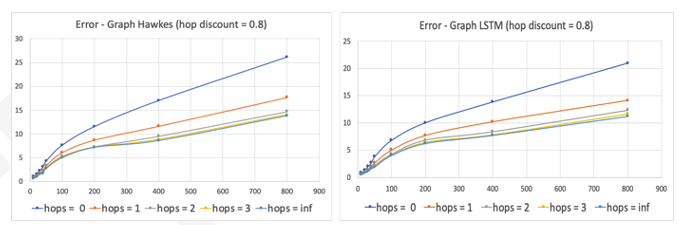
We have tested our approach for modeling the spread of curse words on Twitter. This new approach is compared with an adaptation of Hawkes Point Process to graphs, wherein an entity in a social network may be excited (to utter a curse word) based on the total excitation potential of all the nodes in a k-hop radius around the said node. The proposed approach shows over 30% improvement over the baseline for capturing the positional (who) and temporal (when) dynamics of curse word spread on a social network.
Implications for Defence
This new method offers a method of studying the spread of opinions on a social network. It can be used for what-if analysis when polarizing opinions are injected into a social network through select entities.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
This work is technology readiness level (TRL) 3-4. It provides a technique that can be immediately engineered and applied. However, more experiments may be required for assess the suitability of the technique for a target social network.
Resources and references
- NASN 2021: M. Srivatsa, Diane Felmlee, Roger Whitaker, Supriyo Chakraborthy, Cheryl Giammanco. Modeling Spread of Curse Words on a Social Network
Organisations
IBM US, PSU, Cardiff, ARL