Privacy-Preserving Learning Techniques Based on Generative Adversarial Networks
Military / Coalition Issue
In many situations, coalition partners are available to transfer knowledge among each other in order to reduce the need for training datasets, provided that the privacy of their own datasets is protected.
Core idea and key achievements
Our approach builds on our previous work [1] that uses generative adversarial networks (GANs) to adapt a model learning at a source party for use in a target party that has limited training dataset. Our approach thus allows a source domain to perform transfer learning by domain adaptation based on GANs and at the same time keep private its training dataset. The approach is based on the well-known differential privacy (DP) model; an important parameter in this model is the budget parameter epsilon; recommended values for epsilon are values not higher than 1.
The approach consists of two steps:
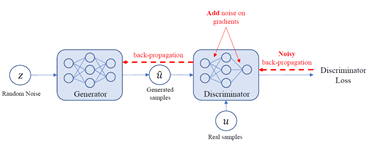
- The first step uses a differentially-private GAN (DP-GAN) to generate a privacy-preserving dataset from the source dataset; the DP-GAN adds noise to the gradient of the discriminator during training.
- The second step uses another GAN to generate the target domain classifier using as input the synthetic dataset and
- the small target domain dataset.
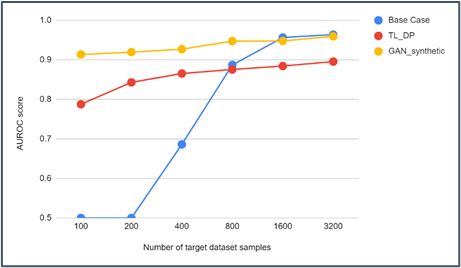
Results show that our approach achieves good accuracy; see the results below for experiments with value of epsilon equal to 0.9833558483.
Implications for Defence
Our approach will support transfer learning, thus providing an approach to address the scarcity of training datasets, while at the same time ensuring data privacy.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
Provides a technique that can be immediately engineered and applied. However, more experiments may be required for assess the suitability of the technique for different application domains and data.
Resources and references
A paper is under preparation.
Organisations
Purdue, IBM US