Joint Reinforcement and Transfer Learning for Distributed Service Configuration in Fragmented Software Defined Coalitions
Military / Coalition Issue
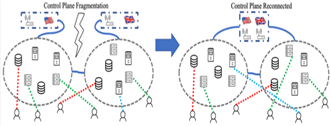
Military missions use infrastructure assets such as communication links, computational servers, data storage, databases, sensors and other resources. Dynamicity and agility of tactical operations demand near real-time configuration and provisioning of these resources. New capability requirements also include efficient re-configuration and sharing of resources among coalition partners, despite infrastructure failures and fragmentation due to attacks or natural system evolutions.
Core idea and key achievements
A new architecture called Software Defined Coalitions (SDC) has been developed, which extends the existing Software Defined Networking (SDN), to support military missions. An SDC is composed of multiple domains, each of which has a set of available resources for sharing among coalition partners. Reinforcement learning (RL) has been proposed to control SDC under given operating conditions. To cope with sudden changes such as SDC fragmentation due to attacks by adversaries or natural system evolutions, a new technique has been developed to join RL with transfer learning (TL) in order to speed up the learning process for the RL for achieving close the optimal performance after SDC domains are reconnected following fragmentation. Thus, the joint RL and TL technique enhances the robustness of the SDC architecture in light of possible fragmentation. The DAIS team has also devised various techniques to realize the SDC capabilities; see related DAIS Outcomes on “Controller Synchronization and Placement,” “Resource Sharing in the SDC,” and “RL for Network Control,” respectively.
Key achievements include the development of:
- Joint RL and TL technique based on generative adversary network (GAN) to produce augmented training data for RL following SDC fragmentation
- Prototype of the proposed RL and TL technique to quantity the speed-up of RL following SDC fragmentation
Implications for Defence
The new technique will enable defence to apply RL for control and sharing of infrastructure assets among armed forces despite possible infrastructure fragmentation. It supports efficient, agile and robust configuration and use of resources, which are unmatched by our adversaries. The joint RL-TL technique is also applicable to other defence systems where the operating environments suddenly change.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
TRL 2/3. Many of the new techniques have been implemented or applied to practical systems, including the joint RL-TL for SDC fragmentation. Further work will help with adapting the techniques to defence environments.
Resources and references
- Zhang, Ziyao, et al. “Efficient Reinforcement Learning with Implicit Action Space.” 4th Annual Fall Meeting of the DAIS ITA, 2020
- Singla, Ankush, Elisa Bertino, and Dinesh Verma. “Preparing network intrusion detection deep learning models with minimal data using adversarial domain adaptation.” In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 127-140. 2020.
- Leung, Kin K., Anand Mudgerikar, Ankush Singla, Elisa Bertino, Dinesh Verma, Kevin Chan, John Melrose, and Jeremy Tucker. “Reinforcement and transfer learning for distributed analytics in fragmented software defined coalitions.” In Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Multi-Domain Operations Applications III, vol. 11746, p. 117461W. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2021.
Organisations
Imperial College, Purdue University, IBM US, ARL and Dstl