Model Pruning for Efficient Federated Learning in Coalitions
Military / Coalition Issue
In a military coalition, partners wish to train a global machine learning model utilizing data from all participating members. However, since the collected data can be sensitive, they have to be kept private to each member. Thus, we use a paradigm called federated learning, where only the model parameters, not the raw data, are shared among participants. To address the problem of limited communication and computation resources on military edge devices, we propose an adaptive pruning method that selects a proper subset of model parameters adaptively over time to accelerate training.
Core idea and key achievements
A machine learning model containing the full parameter set may be too large so that it either exceeds edge devices’ capacities or slows down the training. On the other hand, using too few parameters may cause convergence to a suboptimal final accuracy. We balance the trade-off by constantly estimating the importance of each parameter and finding the subset of parameters that not only preserve the model accuracy but also accelerate the training process. We have achieved:
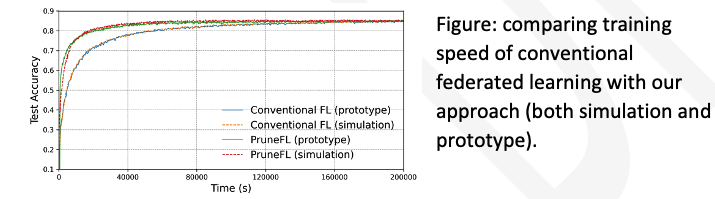
- Automatic acceleration on model training and inference and an implementation of a prototype (see figure below).
- A mathematical proof of the convergence of our algorithm.
Implications for Defence
Our approach accelerates training or adaptation of a machine learning model in a dynamic environment where the edge devices have limited resources. It significantly reduces the time required to reach a target model accuracy, particularly benefiting time-sensitive military tasks.
Moreover, the final model is smaller than the original model, and therefore, it reduces inference time. This is an enabler for real-time processing in some tasks, for example, an object recognition task of a high frame rate video on a surveillance camera.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
Our algorithm is easy to implement – we have developed a prototype and the code is open source.
Resources and references
- Paper: Y. Jiang, S. Wang, V. Valls, B. J. Ko, W.-H. Lee, K. K. Leung, L. Tassiulas “Model pruning enables efficient federated learning on edge devices”, in Workshop on Scalability, Privacy, and Security in Federated Learning (SpicyFL) in Conjunction with NeurIPS 2020, long talk, Dec. 2020.
- Code: https://github.com/jiangyuang/PruneFL
Organisations
Yale University, IBM US, Imperial