Energy Efficient Vector Symbolic Architecture Using ‘In Memory’ Hyper-dimensional Computing
Military / Coalition Issue
The benefits of using symbolic semantic vectors to perform unambiguous communication and decentralized service workflow construction has been described in other key achievements. Edge of network coalition operations, particularly in the context of IoBT operations, are often performed in energy constrained environments where savings in computation energy efficiency can become the limiting factor in determining where to deploy the sensors and services.
Is it possible to use new technologies based on ‘In Memory’ processing to achieve significant energy savings?
Core idea and key achievements
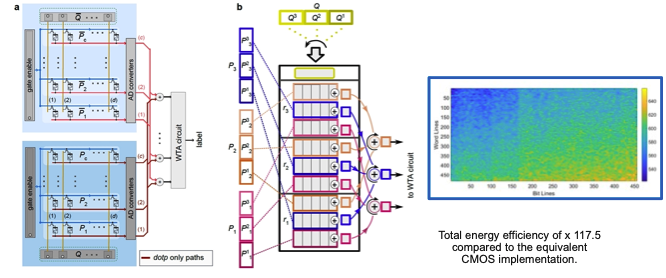
Many of the symbolic semantic vector operations that are required can be performed in a highly parallel fashion using a new generation of ‘In-Memory’ and ‘Near-Memory’ processing devices. We have demonstrated, using an experimental phase change memory device (PCM), that many of the computationally expensive operations that required to perform workflow composition using symbolic semantic vectors can be performed on such devices. Energy savings of greater than 100x what can be achieved when using dedicated CMOS devices have been measured. Ongoing work is focused on re-implementing the logic of our vector mapping and the binding and bundling operations to make greater use of this technology with the aim of implementing all the required operations on a single highly compact and energy efficient device.
Implications for Defence
In memory processing using these new generation of devices to perform vector operations is called hyper-dimensional computing. This new generation ‘In Memory’ processing avoids what is termed the Von Neumann bottleneck and offers the potential for extremely low power processing particularly for vector intensive operations which are becoming increasingly important in Artificial Intelligence and image processing applications.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
The PCM device used in our evaluation is an experimental device developed by IBM Research who are currently developing devices with more memory capacity which we also plan to evaluate. Whilst we have demonstrated their efficacy for energy efficient workflow composition, they are also showing promise in other areas of Artificial Intelligence processing in areas such as image and document classification. Utilising these devices could have a significant impact on future edge of network IoBT/IoT type operations.
Resources and references
- Graham Bent, Christopher Simpkin, Ian Taylor, Abbas Rahimi, Geethan Karunaratne, Abu Sebastian, Declan Millar, Andreas Martens, Kaushik Roy, “Energy efficient ‘in memory’ computing to enable decentralised service workflow composition in support of multi-domain operations,” Proc. SPIE 11746, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Multi-Domain Operations Applications III, 117461Q (12 April 2021); https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2586988
Organisations
IBM UK, Cardiff University