Reinforcement Learning for Military Network Control
Military / Coalition Issue
Efficient and robust control and management of large communication and computation infrastructures for tactical use are critically important to mission success. Traditional optimisation-based control techniques usually over-simplify the original problems and ignore the availability of network operation data. To address these shortcomings, reinforcement learning (RL) has been widely applied for system control. However, state-of-the-art RL often encounters issues such as huge state-action spaces, inefficient knowledge representation, dynamic changes of environments, and violation of underlying mathematical assumptions. These factors greatly increase computational complexity and hinder learning, thus significantly limiting the applicability of RL for national defence.
Core idea and key achievements
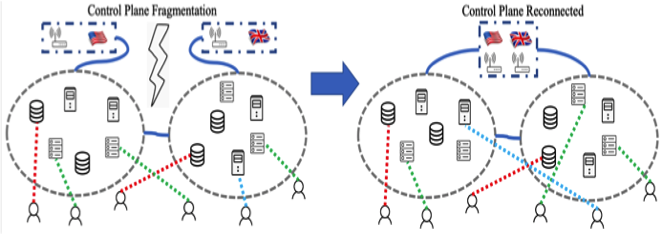
To overcome the inadequacies of optimisation-based control paradigms, RL has been applied to design and control the novel architecture named Software Defined Coalitions (SDC) for sharing infrastructure assets. Specifically, the DAIS team has developed new techniques to address various RL issues for large-scale infrastructures, including state-action space explosion, inefficient knowledge representation of states and actions, learning of sudden changes in operating environments (e.g., SDC fragmentation), and violation of underlying mathematical assumptions. The new techniques not only offer advantages over the optimisation-based methods, but also greatly reduce the computation and learning time, thus extending the applicability of RL to management of very large systems such as SDC. Please also see the related DAIS Outcomes on “Controller Synchronization and Placement,” “Resource Sharing in SDC,” and “Joint Reinforcement and Transfer Learning for Fragmented SDC.”
Key achievements include the development of:
- Efficient deep RL techniques to overcome huge state-action spaces
- Techniques for state-space decomposition and hierarchical RL
- Jointly trained state-action embeddings to speed up learning for RL
- Joint RL and transfer learning (TL) techniques for dynamic changes in operating environments such as SDC fragmentation
- Techniques to solve non-Markov process and extend RL applicability
Implications for Defence
The new techniques will enable defence to apply RL for real-time control and sharing of infrastructure assets among armed forces. They support efficient, agile and robust configuration and use of resources, which are unmatched by our adversaries. The techniques are also applicable to other systems such as radio spectrum sharing in electromagnetic warfare.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
TRL 2/3. Many of the new techniques have been implemented or applied to practical systems, including the joint RL-TL for SDC fragmentation. Further work will help with adapting the techniques to defence environments.
Resources and references
- Zhang, Ziyao, et al. “Macs: Deep reinforcement learning based sdn controller synchronization policy design.” 2019 IEEE 27th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP). IEEE, 2019.
- Pritz, Paul J., Liang Ma, and Kin K. Leung. “Joint State-Action Embedding for Efficient Reinforcement Learning.” arXiv e-prints (2020): arXiv-2010.
- Leung, Kin K., et al. “Reinforcement and transfer learning for distributed analytics in fragmented software defined coalitions.” Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Multi-Domain Operations Applications III. Vol. 11746. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2021.
- Zhang, Ziyao, et al. “Efficient Reinforcement Learning with Implicit Action Space.” 4th Annual Fall Meeting of the DAIS ITA, 2020
- Zhang, Ziyao, et al. “State Decomposition, Distributed and Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for SDC.” 4th Annual Fall Meeting of the DAIS ITA, 2020
- Chen, Zheyu, et al. “Learning Technique to Solve Non-Markovian Decision Process for Networked Resource Allocation .”
Organisations
Imperial College, IBM US, Purdue University, Yale University, Dstl, ARL