Adaptive Federated Learning in Resource Constrained Edge Computing Systems
- Technical achievement: Watch the video
- Demonstration: Watch the video
Military / Coalition Issue
Military data available at dispersed locations is confidential and even coalition partners are reluctant to share. Tactical networks that support analytics services for military operations have limited resources and can change dynamically over time. A key challenge is how to train analytics models using all distributed data at the network edge subject to the bandwidth limitation and data-privacy constraints for coalition partners.
Core idea and key achievements
We have enhanced federated learning (FL) to train analytic models where the private data remains local on the network-edge nodes and only model parameters are shared between different nodes. The new method includes local model updates at the edge nodes and global parameter aggregations by a central server. The technique aims to coordinate these different FL operations to achieve the most efficient model training subject to the limited availability of resources.
To devise the new method, we first derived a fundamental performance bound of FL, which captures the FL performance expressed as a function of different system parameters and settings (such as communication and computation resource availabilities and network topologies). Using the theoretical bound, we developed a control algorithm that adapts the internal steps of FL to best utilize the available resources.
The control algorithm derived from our theoretical analysis determines the best trade-off between local update and global aggregation operations for FL under a given resource budget. Through extensive evaluation by experiments and use of practical datasets, both on a networked prototype system and in a larger-scale simulated environment, we have shown that the proposed approach performs very close to the optimum for various machine-learning models and different data distributions.
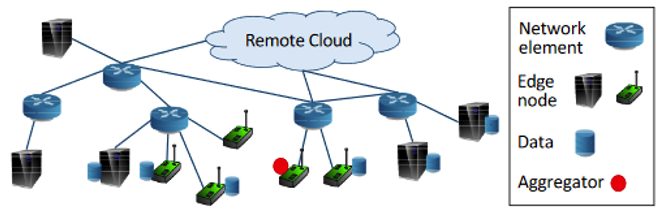
Implications for Defence
This technology enables distributed training or adaptation of analytics models in resource-constrained environments, to allow coalition partners to help each other learn similar tasks without a need of sharing their sensitive data for privacy or lack of communication resources. The new approach provides the cutting-edge capability over our adversaries.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
A set of algorithms are described in published papers and many of them are also available as open source code.
Resources and references
Key papers/patents include:
- Wang, Shiqiang, et al. “When edge meets learning: Adaptive control for resource-constrained distributed machine learning.” IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. IEEE, 2018.
- Wang, Shiqiang, et al. “Adaptive federated learning in resource constrained edge computing systems.” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 37.6 (2019): 1205-1221 which won the IEEE ComSoc Leonard G. Abraham Prize (2021)
- Patent US20190318268A1: Distributed machine learning at edge nodes
- Open source code: https://github.com/IBM/adaptive-federated-learning
Organisations
IBM US, Imperial, PSU, ARL