Compressed Model Updates for Efficient Federated Learning
Military / Coalition Issue
Modern military scenarios largely benefit from agile analytics available in the battlefield. Most of such analytics applications are driven by machine learning models for purposes such as image recognition, anomaly detection, etc. A key challenge in the coalition environment is that data to train these models may not be shareable across coalition boundaries. In addition, new data may be collected during the military operation that can be used to adapt existing models to the current environment. To facilitate model training or adaptation in such challenging situations, federated learning can be applied, which includes multiple rounds of parameter updates between clients and the server. However, since the size of modern deep learning models can be very large, transmitting them across the coalition network with limited bandwidth can be very difficult.
Core idea and key achievements
In this work, we propose a method for compressing the exchanged information between federated learning participants (clients) and the server.
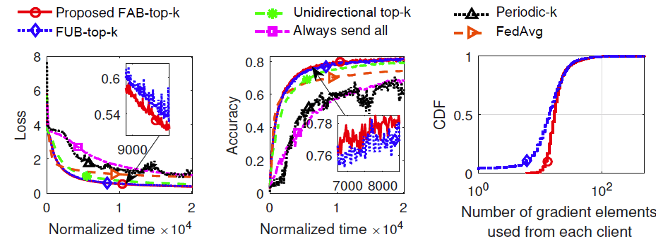
The key idea is a top-k sparsification method that is applied to the communication both from clients to the server (uplink) and from the server to clients (downlink). The algorithm is designed to guarantee a minimum amount of information to be included in each round’s update. In addition, an online learning subroutine finds the near-optimal sparsity (i.e., value of k) over time. Our experiments show that transmitting 1% of model parameters can be sufficient for achieving training convergence in the smallest amount of time.
Implications for Defence
This work is one of the several core technologies for federated learning developed within the DAIS ITA. It allows future military applications to adapt to rapidly changing environments by training/adapting their underlying models to the most up-to-date observations (data), while preserving the privacy and other regulatory constraints in the coalition.
Readiness & alternative Defence uses
A simulation code and a demo illustrating the effectiveness of compressed model updates is available.
Resources and references
- Han, Pengchao, Shiqiang Wang, and Kin K. Leung. “Adaptive gradient sparsification for efficient federated learning: An online learning approach.” 2020 IEEE 40th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). IEEE, 2020.
- Open source code: Adaptive_Gradient_Sparsification_FL
Organisations
IBM US, Imperial